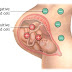
If you are Rh negative and your partner is Rh positive, sensitization (producing antibodies against the fetus) and hemolytic disease can be prevented by injections with blood product called Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg). It will prevent antibodies from forming, but it is not helpful if you have been sensitized and the antibodies already exist in your blood.
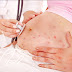
Sensitization can occur any time fetal blood mixes with the mother's blood. This could happen during pregnancy as well as after and abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or amniocentesis. Rhig will usually be given after these events to prevent sensitization and the risk of hemolytic disease in a future pregnancy. The protection from RhIg seems to last only about 12 weeks, so the treatment must be repeated at any event that could result in the mother's Rh-negative blood mixing with that of her fetus.
If a women with Rh-negative blood has not been sensitized, her doctor may recommend that she receive RhIg near near 28 weeks of pregnancy. This takes care of the small number of women who can become sensitized during the last 3 months of pregnancy. If her baby has Rh-positive blood, the mother should be given another does shortly after she gives birth. This treatment keeps the mother from developing antibodies to the Rh-positive cells from her baby that she may have been exposed to during labor and delivery, removing the risk to a fetus in a subsequent pregnancy. Sensitization could occur in the next pregnancy as well, however, so repeat doses of RhIg are given with each pregnancy and birth of an Rh-positive child.
RhIg is safe for a pregnant woman. The only known side effects are soreness where the drug was injected or a slight fever. Both are temporary reactions. RhIg is prepared in a way that kills most viruses and bacteria that might have been in the blood if was made form
Sensitization can occur any time fetal blood mixes with the mother's blood. This could happen during pregnancy as well as after and abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or amniocentesis. Rhig will usually be given after these events to prevent sensitization and the risk of hemolytic disease in a future pregnancy. The protection from RhIg seems to last only about 12 weeks, so the treatment must be repeated at any event that could result in the mother's Rh-negative blood mixing with that of her fetus.
If a women with Rh-negative blood has not been sensitized, her doctor may recommend that she receive RhIg near near 28 weeks of pregnancy. This takes care of the small number of women who can become sensitized during the last 3 months of pregnancy. If her baby has Rh-positive blood, the mother should be given another does shortly after she gives birth. This treatment keeps the mother from developing antibodies to the Rh-positive cells from her baby that she may have been exposed to during labor and delivery, removing the risk to a fetus in a subsequent pregnancy. Sensitization could occur in the next pregnancy as well, however, so repeat doses of RhIg are given with each pregnancy and birth of an Rh-positive child.
RhIg is safe for a pregnant woman. The only known side effects are soreness where the drug was injected or a slight fever. Both are temporary reactions. RhIg is prepared in a way that kills most viruses and bacteria that might have been in the blood if was made form













0 comments:
Post a Comment